Hormonal Imbalance in Women: A Guide to Symptoms, Causes & Treatment

Hormonal imbalance is one of the most popular health issues affecting women, with millions affected globally. It can manifest in various forms, affecting physical, emotional, and mental states. This blog explores the complexities of hormonal imbalance by looking at its causes, signs, and symptoms, as well as management tactics. By understanding these underlying factors coupled with proper treatment measures, women will not only have their hormonal health restored but also gain a better quality of life.
What is Hormonal Imbalance in Women?
Hormonal imbalance is a cumulative term that includes all the conditions linked with hormones. Hormone imbalance in women occurs when there is an excessive level or lack of one or more hormones. Hormones are substances that control different body functions by sending messages through blood to the organs, skin, muscles, and other tissues. The messages tell the body what actions are to be taken when required. Life and health depend on hormones since they affect many bodily processes like metabolism, homeostasis (constancy in the internal environment), growth and development, reproductive functions, sleep cycle patterns, and mood variations.
Over the course of time, significant physiological fluctuations in the levels of hormones occur within women’s bodies, e.g., premenstrual syndrome, pregnancy, and menopause. Certain crucial hormones, such as adrenaline, steroid hormones, growth hormones, insulin, estrogen, or progesterone (a hormone secreted by the ovaries), are likely to be quite imbalanced among women. These imbalances can lead to essential endocrine disorders that often have to be treated medically.
What are the Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance in Women?
Hormonal imbalances have several signs and symptoms, whose manifestations are subject to the individual. For instance, they can vary in intensity, frequency, and duration among people.
The commonest signs of hormonal imbalance in females include menstrual irregularities, skin problems, weight changes, mood changes, breast discharge in non-pregnant women, and decreased work productivity, as well as having low social interactions.
Symptoms: Women with hormonal imbalance usually complaint of any of the following symptoms such as sweating at night, having low libido (low sex drive), being unable to pregnant, experiencing mood fluctuations, having difficulties sleeping, being depressed, noticing changes in appetite, deep voice, changes in heartbeat, breast pain or tenderness, swelling of the face, headaches, poor attention span, bowel and urinary inconsistency, skin and vaginal dryness, rash on the skin surface, neck tumors, excessive hair growth, insomnia (lack of sleep), brittle bones (fragile concentration), hair loss or baldness, perspiration (sweating), altered glucose levels in the blood, eye disorders like conjunctivitis, enlarged clitoris, as well as chronic fatigue syndrome.
Note: All the above-discussed symptoms may not be present in every individual, but they vary depending on the severity and condition of the person.
What are the Hormonal Imbalance Diseases?
Hormonal problems cause numerous health problems. Though many of these hormone dysfunctions need treatment, others can be resolved spontaneously. Here are some typical hormonal imbalance-related diseases:
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a scenario where tissue that is lining the uterus grows externally of this organ.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is an endocrine dysfunction distinguished by irregular menstrual cycles, too much hair growth, acne, and an inability to lose weight.
- Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD): PMDD is an extreme type of premenstrual syndrome characterized by changes in moods, extreme anger, and sadness.
- Hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism is a state in which the thyroid gland does not create sufficient amounts of thyroid hormone.
- Obesity: Obesity is characterized by excessive body fat that may interfere with the balance of hormones.
- Hyperthyroidism: Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by excessive production of thyroxine from the thyroid gland.
- Diabetes: Diabetes is a metabolic disease manifested by increased levels of blood glucose.
- Pituitary disorders: Conditions that affect the pituitary gland, which regulates many hormone productions.
- Adrenal disorders: Conditions impacting the adrenal glands, which generate hormones like cortisol or adrenaline.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions in which the immune system attacks healthy tissues, like in autoimmune thyroiditis or Addison’s disease.
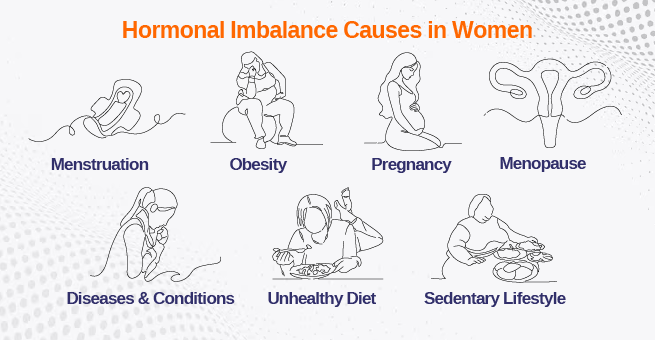
What are the Causes of Hormonal Imbalance in Women?
Hormone imbalances in women have numerous causes; the common factors that tend to cause hormonal imbalance in women are menstruation, puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Other conditions are health conditions, day-to-day life habits, and climatic conditions, as well as malfunctions of the hormone-producing glands. Endocrine glands are present all over the body; they produce and store hormones before releasing them into the pituitary bloodstream, which regulates their action on various organs.
Some of the causes for hormonal imbalance in women include an unhealthy diet, chronic stress, body fatness, tumors on the pituitary gland , type 1 diabetes mellitus , type 2 diabetes mellitus, Prader-Willi syndrome, hereditary pancreatitis, infections with toxins from other sources of pollution, herbicides or pesticides, and severe allergic reactions to anabolic steroids. Turner syndrome metabolism disorders are due to overactive or underactive thyroid phytoestrogens with high levels of glucagon, insulin, and parathyroid hormone concentrations.
A few more less common causes might involve benign tumors, chemotherapy, birth control medications, and hormonal replacement therapies.
How Are Hormonal Imbalances Diagnosed?
Apart from significant symptoms given by the patient, there is no single, comprehensive test that assesses all female hormonal disorders. To find out whether or not one has such a problem, consultation is definitely needed. After a detailed examination, the following diagnostic tests might be suggested:
- Blood tests: The collection of blood samples for laboratory analysis will indicate hormone levels, including estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, thyroid hormones, cortisol, and more. These are useful in identifying cases where there is an imbalance or deficiency.
- Pelvic exam: A pelvic examination reveals any abnormalities in lump, cyst, or tumor forms.
- Ultrasound: This is an imaging technique that uses sound waves to image the uterus, ovaries, thyroid gland, and pituitary gland, among others.
- Specialized Tests: Additional tests may include a glucose tolerance test for diabetes or a bone density scan test when osteoporosis is suspected as a diagnosis, among others, like an x-ray, an MRI, a biopsy, or a thyroid scan, among others.
What are the Options Involved in Hormonal Imbalance Treatment for Women?
The treatment of hormonal imbalance for women involves:
- Hormonal control drugs: Estrogen and progesterone are present in these pills that regulate (and associated disorders) menstrual cycles.
- Anti-androgen therapy: These medications block the hormone androgen and may help diminish male characteristics, severe acne, excess hair growth, or even baldness.
- Hormone replacement therapy: It is possible for women to intake these medications to get temporary relief from menopausal symptoms such as hot flushes or night sweats.
- Vaginal estrogen: A female puts creams containing estrogen on her vaginal tissues during this form of treatment in order to alleviate symptoms. Other remedies for vaginal dryness include estrogen tablets and rings.
- Oral contraceptives: Hormonal regulation in females suffering from conditions such as PCOS can be achieved through birth control pills.
- Antidepressant usage: Mood disorders caused by hormonal imbalance may require antidepressants to be prescribed.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): For women with PCOS who are trying to conceive, assisted reproduction technologies like IVF can often prove successful.
- Others: Symptomatic approaches based on diabetes, thyroid, obesity, and immune-related medications are advised in some cases.
In addition to the above-discussed practices, lifestyle modifications, hormone-balancing foods, and dietary changes also play a significant role in managing the hormonal imbalances in women.
How to Prevent Hormonal Imbalance in Women?
Adopting certain lifestyle habits or changes can aid in avoiding hormonal imbalances among women and younger females. Such habits include:
- Managing stress through self-regulation techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, positive visualization, and meditation.
- Keeping body weight healthy.
- Eating food that is balanced and nutritious.
- Engaging in exercise on regular occasions.
- Cutting down on sweetened items as well as packaged ones.
- Reducing household cleaners’ use with toxic elements.
- Steer clear of spicy foods and drinks that may trigger hot flashes.
- Replacing older non-stick pans with ceramic pots while cooking.
- Taking organic fruits and vegetables free from pesticide sprays.
- Also scheduling regular checkups to monitor health status.
What are Hormone Balancing Foods?
Hormone-balancing foods are the foods that have a significant role in supporting hormonal health in women. Here are some foods believed to balance hormones:
- Green vegetables: These are an excellent source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as fiber, which serve as stimuli for hormone production and regulation.
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseed is a good source of lignans that have estrogenic effects.
- Lignans: Lignans help to balance progesterone levels and avoid hormonal imbalance, hence reducing the risk of conditions associated with it.
- Whole grains: Whole grains, including oats, quinoa, and brown rice, provide fiber that promotes hormonal balance.
- Berries: Berries, including blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries, are rich in antioxidants that counter the effects of unhealthy living.
- Healthy fats: Healthy fats such as those found in avocados, seeds, and nuts control hormone production; they also prevent inflammation, hence improving moods, thereby leading to balanced hormones.
- Lean proteins: Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, and beans are amino acids that assist with their production while preventing hormone-related diseases or disorders.
Conclusion
Hormonal imbalance is a prevalent health issue that can significantly affect a woman’s quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help women manage their hormonal health. Medical interventions like hormone therapy, birth control pills, and antidepressants may be necessary, requiring consultation with a healthcare provider.
Yashoda Hospitals provides personalized care for hormonal imbalance, with expert gynecologists and endocrinologists offering comprehensive solutions from diagnosis to treatment. Their commitment to achieving hormonal balance and improving overall well-being allows patients to take control of their health.
Have any questions or concerns about your health? We’re here to help! Call us at +918065906165 for expert advice and support.
















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More