Is Your Liver at Risk? The Truth About Viral Hepatitis
1. What is Viral Hepatitis? Let’s discuss
3. Hepatitis A (HAV) Preventable, Treatable, and Temporary
4. Hepatitis B (HBV) A silent infection that deserves your attention….!!!
5.Hepatitis C(HCV) Cure it in weeks, not years…!!
6. Hepatitis D(HDV) Rare but Serious….!!!
7. Hepatitis E(HEV) Personal Cleanliness, Keep it away….!!!!
What is Viral Hepatitis? Let’s discuss
The liver, located in the right upper quadrant just below the diaphragm, plays a crucial role in metabolism and overall health. It is responsible for producing essential proteins, biochemicals, and hormones necessary for digestion and other bodily functions. In addition, the liver detoxifies harmful substances, stores and converts nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and serves as the site for the breakdown of aging red blood cells. Hepatitis is a disease wherein there is an inflammation (swelling of any organ or tissue that is injured or infected) in the liver, which leads to multiple major health issues like serious liver damage and cancer of the liver, leading to death of the patient in some cases.
Hepatitis, or inflammation of the liver, can be classified in two main ways: its duration (acute or chronic) and by what causes it (such as viruses, alcohol, or autoimmune conditions). Understanding these classifications enables doctors to provide the right treatment and care.
Hepatitis, which occurs suddenly and does not last for a long time (resolved within 6 months), is termed acute hepatitis. Hepatitis that lasts for a long time (more than 6 months) and leads to gradual deterioration of patients’ condition into serious liver-damaging conditions like cirrhosis of the liver, and liver cancer is termed chronic hepatitis.
Based on what causes it, Hepatitis can be classified into Viral hepatitis, where the virus is the main cause of hepatitis. Viral hepatitis is mainly caused by five types of viruses, and based on duration, it is generally chronic or acute.
Non-viral hepatitis is again caused by various scenarios, such as hepatitis due to excessive alcohol consumption, and taking high dosages of medications like acetaminophen, which are categorised under this, also termed as alcohol-induced hepatitis or drug-induced hepatitis. Autoimmune hepatitis is a form of hepatitis where liver cells are targeted by the body’s immune system. Irregular metabolism and hereditary conditions leading to hepatitis, where hepatitis is caused by a deficiency of biochemicals in the body, like alpha-1-antitrypsin, and due to genetic disorders like Wilson’s disease, are categorized into this type. Also, other diseases wherein bile juice accumulates in the liver(cholestasis), Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD), and metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), most often lead to hepatitis.
Types of Viral Hepatitis
As defined earlier in the blog, hepatitis caused by viruses is termed viral hepatitis, a very common and complicated type of viral liver infection. To date, a total of six viruses known to cause viral hepatitis have been identified, which have been alphabetically named based on when they were first identified, namely.
Hepatitis A(HAV)
Hepatitis B(HBV)
Hepatitis C(HCV)
Hepatitis D(HDV)and
Hepatitis E (HEV)
Hepatitis A (HAV) Preventable, Treatable, and Temporary
Hepatitis A is a type of viral hepatitis as a result of infection by the Hepatitis A virus (HAV), a type of hepatovirus belonging to the picornaviridae family.
Hepatitis A virus is very infectious, attacking the human body through many mediums, but most commonly this type of viral hepatitis infects the human body through two ways: one is by ingesting contaminated food (raw shellfish) and contaminated water. That contamination can occur at any stage of food being grown, processed, handled, and cooked. Viral hepatitis by HAV infections can also occur when a normal person comes into direct contact with objects used by an infected patient, and through sexual intercourse.
Patients infected with HAV viral hepatitis typically exhibit the following signs within 2 days to 7 weeks of infection, like
- Jaundice, wherein the skin and eyes generally turn yellow
- Pain in the gut area
- Loss of hunger
- Unwillingness to eat anything and upset stomach
- Skin itching
- Change in poop colour and urine colour
- Joint pain
- High Fever
- Tiredness
These symptoms are typically not exhibited by children, whereas in older patients, these symptoms can be serious. Based on duration, HAV viral hepatitis is generally an acute one.
There is no perfect treatment for HAV viral hepatitis once an individual is infected with it. A physician only provides care to cure the symptoms that are exhibited by the individual until they no longer exist. Frequent medical examinations are conducted to check the severity of infection on the liver and if the recovery process is on course. Patients showing these signs and symptoms should take good rest, completely avoid alcohol, consume high-calorie food, and drink enough water to stay hydrated.
Vaccination against HAV viral hepatitis was found to be beneficial in 95% of adult patients for 20 years, and in 85% of children for 15-20 years. Vaccination is usually planned in two phases for children, with the first dose provided from 12-23 months and the second dose between the ages of 2-4 years. In adults, the time between two doses generally ranges from 6 months to 18 months.
HAV viral hepatitis is usually not associated with any long-term complications as such but in patients with existing liver problems and older patients with severe symptoms, it has resulted in long-term liver failure leading to transplantation.
Hepatitis B (HBV) A silent infection that deserves your attention….!!!
Viral hepatitis caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) leads to Hepatitis B infection, a virus belonging to the hepadnavirus family. An individual can become ill due to Hepatitis B by exposure to diseased patients’ body fluids, such as blood, spit, and semen. Even if the Hepatitis B-affected patient does not exhibit any known signs, he still has the potential to infect a healthy individual. Most common ways the infection is spread are due to
- Sharing of medical instruments like syringes, needles, etc.
- Using the same toothbrushes, razors.
- Directly exposed to open sores or the skin of an infected individual
- Sexual intercourse
- Unhygienic healthcare facilities
- Mother to the newly born infant
Hepatitis B virus symptoms often range from mild to severe, depending on the patient infected. In children below 5 years, it shows no signs, whereas in adults above 30 years of age, the indications range from mild to severe. The following signs may appear anytime between the first 90 days of infection and can last up to 6 months. General indications of this form of viral hepatitis are:
- Fever
- Tiredness that may last from weeks to months
- Decreased desire to have food
- Dark urine and light coloured feces
- Vomiting
- Uneasy feeling of being sick (Nausea)
- Jaundice (yellow colouration of skin and eyes)
Viral hepatitis of the Hepatitis B virus is known to be both acute(lasting less than 6 months) and chronic(lasting more than 6 months) in nature. Chronic hepatitis was found to be generally prevalent in about 90% of infants infected with it, leading to serious liver damage, liver cirrhosis (permanent scarring and harm to the patient), liver cancer, and death of the patient.
Vaccination is a very important option for a serious form of viral hepatitis like Hepatitis B. It is generally recommended by doctors to take the vaccination for this virus within 24 hours of birth. Also, Hepatitis B immunoglobulin injection prepared by using antibodies from human blood was found to be quite useful in the treatment of Hepatitis B infection.
Acute Viral hepatitis B infections are often managed using pain medications, intravenous fluid, and nutrition (administration of fluids and food using a tube placed in the veins of humans).
Chronic form of Viral Hepatitis B infection is managed using antiviral medications like Adefovir dipivoxil, Entecavir, Lamivudine, Telbivudine, Tenofovir alafenamide, or Tenofovir disoproxil. Other treatments of this infection, especially in children with chronic hepatitis, include multiple injections of Interferon alfa, Pegylated interferon, namely antibodies, likely to be administered over a period of 6-12 months.
Ultimately, due to the gradual deterioration of the general health of patients, which is observed in this form of Viral hepatitis B infection, liver transplant is highly recommended along with changes in lifestyle like avoiding alcohol, eating healthy foods with less amount of sugar, and taking medicines usually after consultation with a medical professional.
Complications due to the acute form of Viral hepatitis B infection include confused feelings, mood swings, uncontrollable behaviour, decreased concentration and memory, and being less attentive to surroundings. Contrastingly, the chronic form of Viral hepatitis B infection is more serious and, as mentioned in the above sections, usually leads to complete liver failure (Cirrhosis), Liver cancer, and can lead to infection by other types of Viral hepatitis like Hepatitis D.
Hepatitis C(HCV) Cure it in weeks, not years…!!
Another form of Viral Hepatitis is Hepatitis C caused due to infection by Hepatitis C virus(HCV), a type of hepacivirus belonging to the family flaviviridae. Similar to Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B infections, Hepatitis C infections are mainly caused by coming into direct contact with bodily fluids like the blood of the affected patient, which takes place by following methods like :
- Sharing of needles and syringes, especially among drug addicted individuals
- Use of an infected needle in healthcare institutions
- Coming into direct contact with sores on the body of the affected individual
- Sharing of day-to-day objects and having unprotected sexual intercourse
Viral Hepatitis C virus is not spread through coughing, sneezing, kissing, or breastfeeding an infant. A large percentage of patients, about 80% of them, do not show any symptoms. The affected patient can show gradual signs in a time ranging from 2 weeks to 6 months, with observations like
- Fever
- Tiredness that may last from weeks to months
- Decreased desire to have food
- Pain in joints
- Dark urine and light coloured feces
- Vomiting
- Uneasy feeling of being sick (Nausea)
- Jaundice (yellow colouration of skin and eyes)
Chronic patients of the Hepatitis C virus affected individuals do not show any signs or symptoms until it’s too late, often 10-30 years from the first point of infection. After this period, as liver functions start to get affected, the patient exhibits the following types of problems:
- Loss of hunger
- Uneasy feeling (Nausea)
- Tiredness
- Pain in the upper right side of the stomach area
- Spider angiomas – Spider-like veins appear on the skin
- Redness of palms and itching
- Yellow bumps on skin
- Weight loss
- Out-of-control muscle movements leading to twitching
- Confusion and mood changes
- Menstrual cycle changes in female patients
- In male babies, enlarged breast tissue and shrunken testicles have been noticed.
- Swollen belly (ascites), swollen limbs, and face (edema)
- Easy loss of blood through both vomit and poop
- Breath shortness
The acute form of Viral Hepatitis C infection can be easily treated 95% of the time within 8-12 weeks, depending on the genetic information virus that has caused the infection, the health condition of the liver, and if the patient has any other health issues. Chronic form of Hepatitis C infection is commonly treated using various antiviral medications like Daclatasvir, Elbasvir-Grazoprevir, Glecaprivir/ Pibrentasvir, Ledipasvir/Sofusbuvir, Ombitasvir/Paritaprevir/dasabuvir, Simeprevir, Sofusbuvir/vel-patasvir. Old medications like Ribavirin, Peginterferon alfa 2a, and Peginterferon alfa-2b have also been found useful to alleviate the symptoms of chronic Hepatitis C virus infection.
Hepatitis C condition usually transforms itself into a chronic form most often than not in about 85% of patients who are infected with it. If timely treatment is not obtained, then it generally leads to permanent liver damage (Cirrhosis) and liver cancer.
Hepatitis D(HDV) Rare but Serious….!!!
Hepatitis D viral hepatitis, is a form of viral hepatitis that develops when a patient is already carrying the Hepatitis B virus. Also known as Hepatitis Delta Virus (HDV), it belongs to a family known as Riboziviriya. The Hepatitis D virus needs the Hepatitis B virus to survive, so a Hepatitis D-infected patient already has a Hepatitis B infection. Usually, the infection is of two types. One situation is where the affected individual at the same time has both Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D infection. Another type is an affected individual who has Hepatitis B infection, then after some time, he develops the Hepatitis D infection. Usually, the signs of Hepatitis D infection are:
- Jaundice (Yellow coloration of skin and eyes).
- Pain in the stomach and the belly region
- Tiredness
- Joint Pain
- Change in colour and volume of stool and urine
- The symptoms of Hepatitis D, when combined with Hepatitis B, can worsen patients’ condition.
As we have discussed earlier in the above paragraphs, the Hepatitis D virus needs the Hepatitis B virus to affect the patient. Therefore, vaccination for Hepatitis B is usually given after 24 hours of birth, also greatly limiting the chance of a Hepatitis D infection.
Hepatitis D is known to be a superinfection as it affects a patient in combination with another virus. Once infected, more than 90% of patients suffer long-term damage to the liver, namely liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis E(HEV) Personal Cleanliness, Keep it away….!!!!
Hepatitis E is a type of viral hepatitis as a result of infection by the Hepatitis E virus (HEV), belonging to the Hepeviridae family. Similar to Hepatitis A virus, Hepatitis E virus was mainly found to attack the patients through contaminated and unhygienic food, water. In addition to this, infection was found to be prevalent in patients who consume undercooked meat and food, including stale shellfish caught from not-so-clean water sources.
Similar to other forms of Hepatitis, Hepatitis E viral hepatitis also shows the same signs:
- Fever
- Tiredness that may last from weeks to months
- Decreased desire to have food
- Pain in joints
- Dark urine and light coloured feces
- Vomiting
- Uneasy feeling of being sick (Nausea)
- Jaundice (yellow colouration of skin and eyes).
Hepatitis E cures itself on its own in about 4-6 weeks, as usually doctors treat the signs of disease, as in the case of Hepatitis A. Adequate rest, eating healthy food, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding alcohol can help prevent this form of Viral hepatitis.
Hepatitis E can be a challenging infection to deal with when it infects pregnant women and older patients with weak immune systems.
Negotiating Viral Hepatitis Your Path to a Healthy Life
Viral Hepatitis today is a major global health concern, especially in underdeveloped countries with poor hygiene, contaminated food and water bodies, unsafe medical health centres with rapid spread of infection, and no strict quarantine measures implemented between healthy and infected individuals.
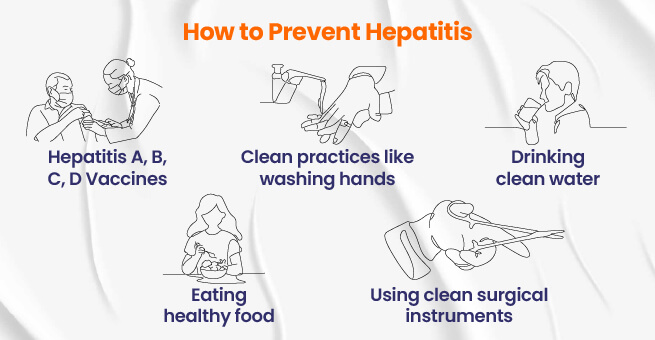
This can be prevented by following a strict vaccination program, especially for Hepatitis A, B, D, and E subtypes. Protecting oneself and others needs to be practiced with strict hygiene programs and guide the population at risk about safe practices to stop the infection of Viral hepatitis.
Have any questions or concerns about your health? We’re here to help! Call us at +918065906165 for expert advice and support.
FAQ’s
Is Hepatitis a Viral Disease?
Yes, Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. Viral hepatitis is caused by five main types of viruses, namely Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D, and Hepatitis E.
How to reduce the viral load in Hepatitis B?
To reduce the viral load in Hepatitis B, a type of viral hepatitis, doctors suggest antiviral medications such as tenofovir, entecavir, or interferon injections. This medication stops the multiplication of the virus, thereby reducing the damage caused to the liver. Patients infected should modify their lifestyle and avoid alcohol, maintain a healthy weight, have a balanced diet, and reduce stress.
Which type of viral hepatitis does not have a chronic carrier state?
Hepatitis A and Hepatitis E are two types of viral hepatitis that usually do not progress to a chronic state (lasts more than 6 months). Both are acute infections that usually resolve within a few weeks of symptom treatment.
How is viral hepatitis transmitted?
Viral hepatitis spreads in different ways depending on the type of virus. Hepatitis A and E mostly spread through close contact with the infected patient, and fecal-oral routes via contaminated food, water resources. In contrast, Hepatitis B, C, and D are spread through Blood and Body fluids, or from mother to child.
Is viral hepatitis contagious?
Yes, viral hepatitis is contagious. Different types of Viral hepatitis viruses spread through different means; some spread through fecal-oral routes via contaminated food, water resources. Meanwhile, in some other types, they are spread through infected blood or body fluids.











 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More