Is Your Liver in Trouble? Hidden Enzyme Clues You Shouldn’t Ignore!

In today’s world of phone alerts and notifications, your liver has its way of sending signals through enzymes. You won’t get a call or text, but a slightly high number in your blood test? That’s your liver’s gentle way of asking, “Something’s not right; please pay attention.”
In this blog, we navigate you through all the details about liver enzyme tests, from what they mean to why they rise, and how to manage them naturally. Whether you’ve recently received abnormal test results or simply want to better understand your liver, this information can help you take the best steps toward recovery.
Liver Enzymes: Tiny Proteins, Big Responsibilities
Liver enzymes are tiny proteins, yet they hold huge responsibilities, from digestion and detoxifying harmful substances to balancing the hormones and keeping your body’s functions running smoothly—the so-called unsung heroes of metabolism. Some of the common liver enzymes include Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Alanine transaminase (ALT), Aspartate transaminase (AST), & Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). However, when there is swelling or liver damage, these enzymes leak into the bloodstream, contributing to high levels on blood tests, which indicate that your liver is under stress and needs medical attention.
What is a Liver Enzyme Blood Test, and Why Is It Done?
Liver Enzyme Test, one of the common Liver function tests, involves a small blood test performed to evaluate the levels of liver enzymes that leak into the bloodstream due to an injury or infection, or an underlying liver condition. It is essential to note that even if you feel fine, high enzyme levels may indicate underlying liver issues. Therefore, early diagnosis through routine checks or early reports to doctors when you experience certain symptoms can help in detecting liver issues at the earliest and can prevent the risk of further complications.
| Liver enzyme | Normal ranges (u/l) | High levels indicate |
|---|---|---|
| AST (Aspartate aminotransaminase) | 8 to 48 units per liter | Liver or muscle damage |
| ALT (Alanine aminotransaminase) | 7 to 55 units per liter | Hepatitis, fatty liver, or alcohol-induced |
| GGT (Gamma-glutamyl transferase) | 8 to 61 U/L. | Liver or bile duct issues |
| ALP (Alkaline phosphatase) | 40 to 129 U/L. | Bile duct or certain bone diseases |
Why Are Your Liver Enzymes High? Uncover the Root Causes
It is important to remember that these elevated levels of enzymes aren’t just lab results; they can be anything from a fatty liver to a medication side effect or hidden inflammation. So it’s a high alert to pause, listen, and act to address the underlying root cause to prevent long-term harm and support real recovery and not just temporary relief.
- Certain Medications: while the liver plays a major role in the metabolism of drugs, helping the body in eliminating them, the use of certain medications, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs, antibiotics, and painkillers, for a long period, can add stress to the liver & cause damage.
- Fatty Liver: Due to damaged liver cells resulting from excessive alcohol consumption or an unhealthy diet, etc., it is obvious that the liver enzymes are elevated in individuals with underlying fatty liver disease.
- Infections: Certain infections, including viral hepatitis, contribute to high levels of liver enzymes as they affect the liver cells directly.
- Alcohol consumption: Excessive & regular alcohol consumption can further damage the liver tissue, further leading to high levels of liver enzymes in the blood.
- Genetic conditions: Certain hereditary conditions, such as hemochromatosis (iron overload) or Wilson’s disease (copper buildup), cause liver damage and result in elevated enzyme levels.
- Bile duct obstruction: certain underlying conditions, such as gallbladder stones, cause bile flow obstruction, and the excess bile remains in the liver and irritates the liver cells, leading to high levels of enzymes.
Symptoms of High Liver Enzymes
Ideally, although there are high levels of liver enzymes in your bloodstream, you may not experience any symptoms. At times, if the underlying cause is any liver condition or its damage, you might experience the following symptoms.
- Pain or swelling in the abdomen.
- Urine appears dark colored.
- Feeling extremely tired
- Yellow discoloration of the skin or eyes
- Itchy feeling on the skin
- Light-colored stools
- Feeling less hungry
- Swelling in the legs
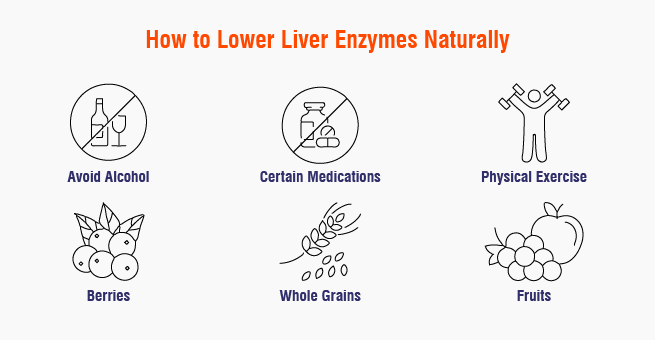
How to Lower Liver Enzymes Naturally
Consuming a liver-friendly diet that improves the liver’s functioning or fights against oxidative stress in the liver. Studies have proven records of certain food items that aid in restoring liver function and help you recover soon.
- Coffee: While excessive caffeine is harmful, it is believed that drinking one to two cups of coffee per day can reduce the risk of viral hepatitis.
- Nuts: while a handful of nuts, including walnuts, is a source of energy and has huge benefits, they contain antioxidants that help in restoring the liver’s health.
- Greens: Leafy vegetables or cruciferous veggies, including broccoli and cauliflower, have cleansing or detoxification properties, thereby flushing out toxins and reducing inflammation and damage.
- Berries: Add Blueberries and cranberries as a part of your snack, as they can decrease liver cell damage and thereby reduce liver enzymes leaking in your bloodstream.
- Whole grains: Consume Oats and brown rice, as they improve digestion and liver metabolism.
- Fruits: Fruits are rich in fiber, and grapes packed with antioxidants can reduce fat accumulation in the liver. Furthermore, watermelons and oranges are also good fruits to add to your plate to improve liver health.
Lifestyle Tips:
- Apart from consuming a diet that is liver-friendly, it is important to avoid foods that can add stress to your liver, such as processed foods and fried foods.
- Regular physical exercise to maintain a healthy body weight
- Avoid consuming excessive alcohol to prevent alcohol-induced liver damage.
- Practice hygiene—wash hands to reduce infection risks from contaminated food.
- Avoid long-term use of certain medications, including painkillers or any herbal supplements.
When to See a Doctor?
- You have been on painkillers or herbal supplements for a long time.
- You experience symptoms, such as abdominal pain, vomiting, yellow discoloration of eyes or skin, etc.
- Your routine blood test shows elevated liver enzyme levels.
Depending upon your personal medical history and the symptoms, your doctor might suggest a further imaging scan, such as an ultrasound, etc. Furthermore, if they suspect any underlying liver cancer, a small biopsy sample is collected for further evaluation.
Fatty liver has been one of the leading concerns in most individuals, but most of them go unnoticed, as they may not develop any symptoms. Liver enzymes can silently be elevated, and you may still feel fine; therefore, routine checkups help in the early diagnosis of any liver conditions. At Yashoda Hospitals, we make sure these early signs are not missed; we ensure timely diagnosis and effective treatment to protect your liver with our expert doctors and advanced care.
Have any questions or concerns about your health? We’re here to help! Call us at +918065906165 for expert advice and support.














 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More